We tap into Noble USDC Bridge to access Interchain native USDC stablecoin across all major blockchains- with low fees and almost instant settlement
How it works….
Blockchain networks often operate in siloed environments and cannot natively communicate with one another. While some ecosystems, such as Cosmos, use built-in protocols like the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol to enable data transmission between their appchains, direct communication between isolated networks, such as Ethereum and Avalanche, remains infeasible.
Traditional bridges exist to address this limitation by enabling the transfer of digital assets, such as USDC, across blockchains. However, these bridges come with significant drawbacks. Two common methods, lock-and-mint bridging and liquidity pool bridging, require locking USDC liquidity in third-party smart contracts. This approach reduces capital efficiency and introduces additional trust assumptions.Design Approach
As a low-level primitive, CCTP can be embedded within any app or wallet – even existing bridges – to enhance and simplify the user experience for cross-chain use cases. With USDC circulating across a large number of blockchain networks, CCTP can connect and unify liquidity across disparate ecosystems where it’s supported.
CCTP is built on generalized message passing and designed for composability, enabling a wide range of use cases. Developers can extend its functionality beyond just moving USDC between blockchains. For example, you can create a flow where USDC is sent across chains and automatically deposited into a DeFi lending pool after the transfer, allowing it to generate yield in an automated manner using Hooks. This experience can be designed to feel like a seamless, single transaction for the end user.How CCTP works
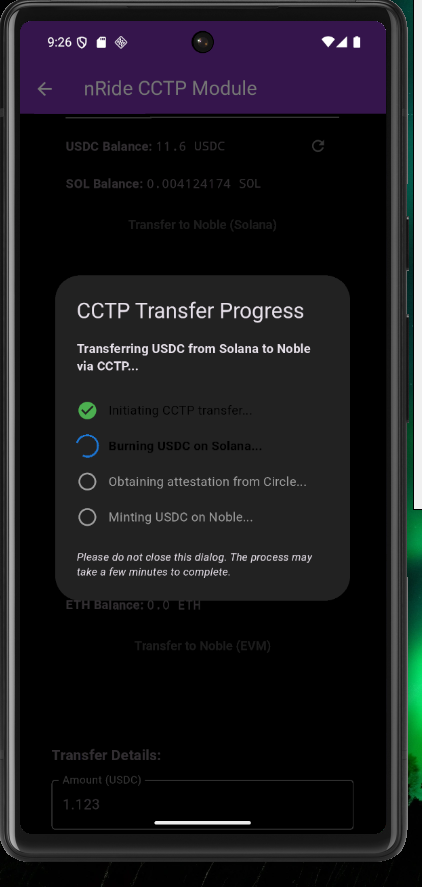
CCTP enables seamless and secure transfers of USDC across blockchains through two transfer methods: Standard Transfer and Fast Transfer. Both involve burning USDC on the source chain and minting it on the destination chain, but the steps and speed differ:Standard Transfer (Available in CCTP V1 and CCTP V2)
Standard Transfer is the default method for transferring USDC across blockchains. It relies on transaction finality on the source chain and uses Circle’s Attestation Service to enable standard-finality (hard finality) transfers. The process includes the following steps:
- Initiation. A user accesses an app powered by either CCTP V1 or CCTP V2 and initiates a Standard Transfer of USDC, specifying the recipient’s wallet address on the destination chain.
- Burn Event. The app facilitates a burn of the specified USDC amount on the source blockchain.
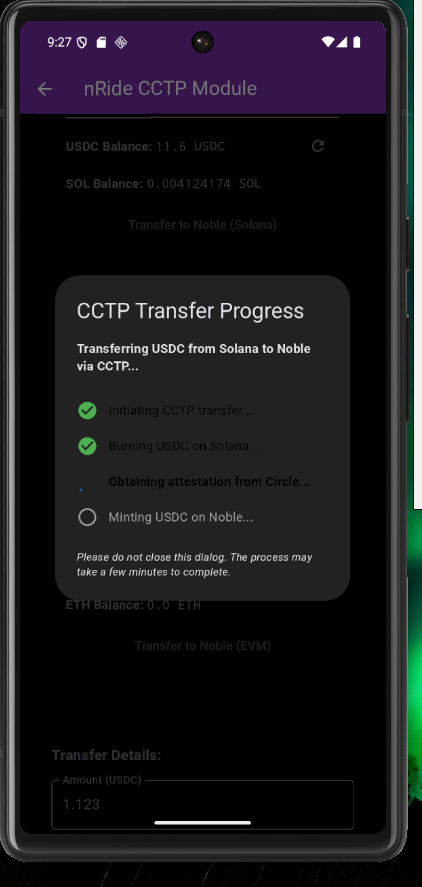
- Attestation. Circle’s Attestation Service observes the burn event and, after observing hard finality on the source chain, issues a signed attestation. Hard finality ensures the burn is irreversible (about 13 to 19 minutes for Ethereum and L2 chains.)
- Mint Event. The app retrieves the signed attestation from Circle and uses it to mint USDC on the destination chain. For CCTP V2, no fee is currently collected onchain during this step, but that may change with advance notice. For details, see the CCTP fee schedule.
- Completion. The recipient wallet address receives the newly minted USDC on the destination blockchain, completing the transfer.
Standard Transfer prioritizes reliability and security, making it suitable for scenarios where finality wait times are acceptable.Fast Transfer (Available only in CCTP V2)
Fast Transfer is an advanced feature of CCTP V2 designed for speed-sensitive use cases. It leverages Circle’s Attestation Service and Fast Transfer Allowance to enable faster-than-finality (soft finality) transfers. The process involves the following steps:
- Initiation. A user accesses an app powered by CCTP V2 and initiates a Fast Transfer of USDC, specifying the recipient’s wallet address on the destination chain.
- Burn Event. The app facilitates a burn of the specified USDC amount on the source blockchain.
- Instant Attestation. Circle’s Attestation Service attests to the burn event after soft finality (which varies per chain) and issues a signed attestation.
- Fast Transfer Allowance Backing. Until hard finality is reached, the burned USDC amount is backed by Circle’s Fast Transfer Allowance. The Fast Transfer Allowance is temporarily debited by the burn amount.
- Mint event. The app retrieves the signed attestation from Circle and uses it to mint USDC on the destination chain. A fee is collected onchain during this process.
- Fast Transfer Allowance Replenishment. Once the burn reaches finality on the source chain, the corresponding amount is credited back to Circle’s Fast Transfer Allowance.
- Completion. The recipient wallet address receives the newly minted USDC on the destination blockchain, completing the transfer.
Fast Transfer is ideal for low-latency use cases, enabling USDC transfers to be completed in seconds while maintaining trust and security via Circle’s Fast Transfer Allowance.
Latest News & Articles




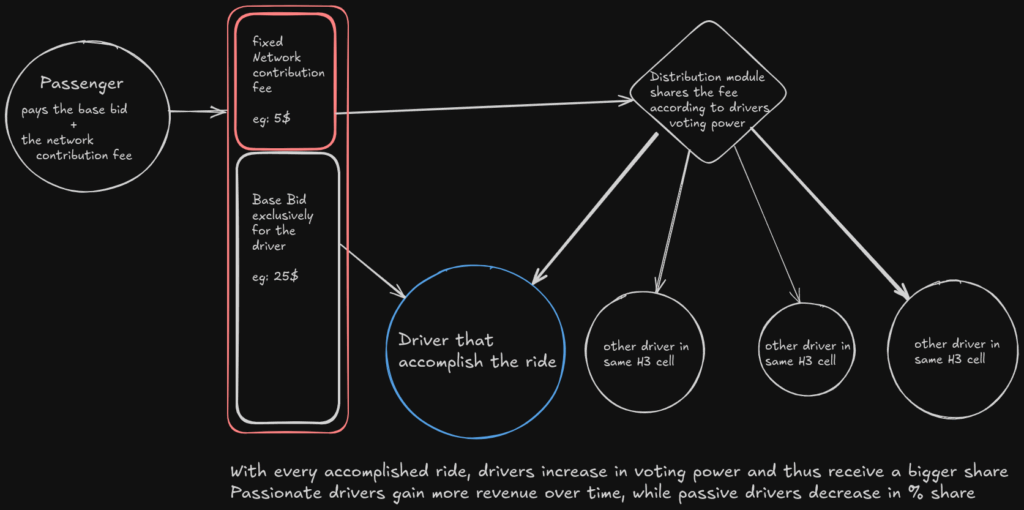
Programmable Money Payments to rewards nRide mobility partners
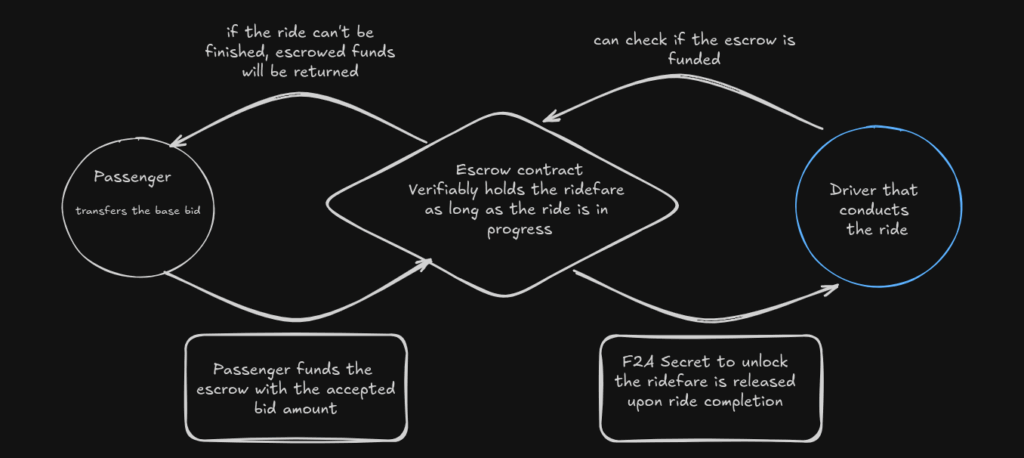
Escrowed Online-Payment using the USDC Stablecoin
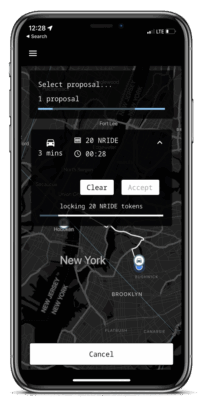
To ensure a safe way of payment for both parties, the ride-fare is being locked in a blockchain secured escrow smart-contract
This ensures that the driver will receive his payment after a successfull ride, as well as a guaranteed refunding to the passenger, if the driver won’t show up or the ride can’t be finished


EURC supported in future soon…
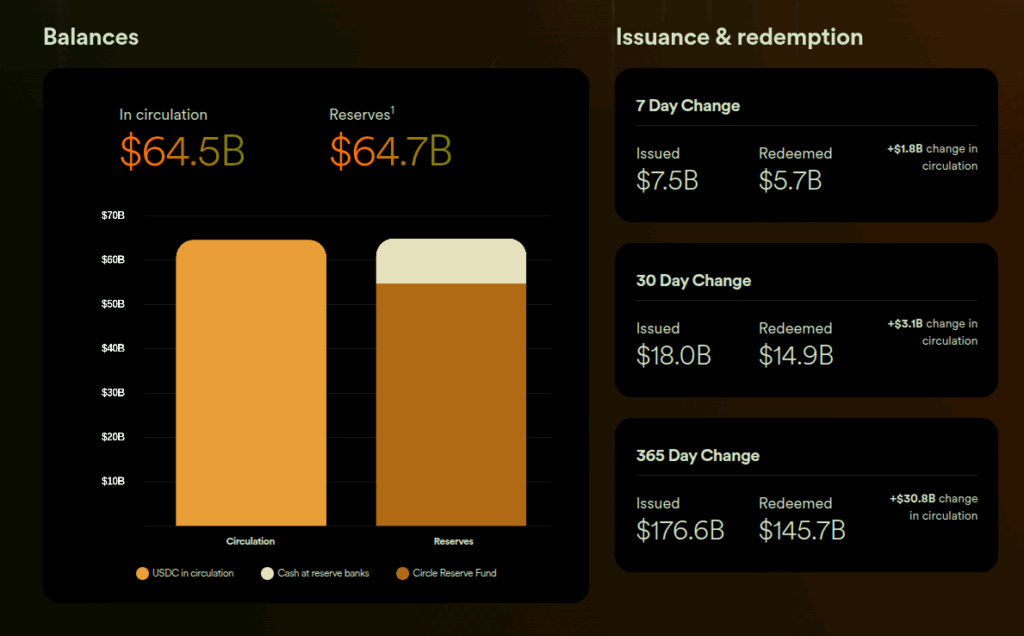
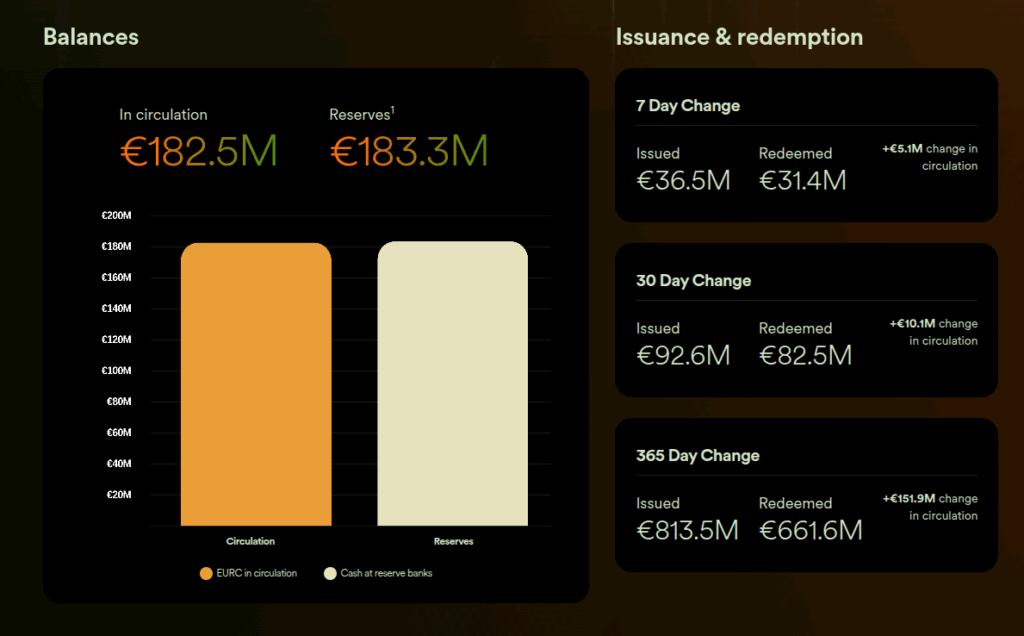
USDC and EURC are fully backed by highly liquid fiat reserves held separately from Circle’s operating funds at leading financial institutions for the benefit of our stablecoin holders. As part of our strong commitment to transparency, we’ve issued reports on all reserve assets since 2018, along with SEC filings in 2021 and 2022.

Legal certainty is the essential fundament for drivers, that need to rely on accredited payment methods.
nRide will manifest the USDC stablecoin as the global currency standard for public urban transport services
How it works
Disrupting centralized and isolated userbases with a trustless p2p network design, secured by blockchain technology
nRide is a pioneering decentralized ride-hailing platform that is poised to disrupt the traditional ride-hailing industry. Built on blockchain technology and smart contracts, nRide enables a trustless and secure ride-hailing experience that empowers drivers and riders to interact directly, without the need for a third party to facilitate the transaction.
Mobile App
Next-Generation of web3 Mobile Apps
The nRide application is the first implementation of the nRide protocol, which includes all the features and functionalities covered in the whitepaper. Get early access to the application, and explore the potential of nRide.
Sovereign Self-Custodial in-App Wallet ensures you don’t need to grant any permissions from your main wallet.
powered by:
Our Services
A new way to provide a trustless marketplace for mobility solutions
The nRide project was founded in October 2021 at the Gitcoin GR11 Hackathon sponsored by NKN, where it won a prize for its innovative approach to peer-to-peer ride-hailing. At the beginning, the idea was to build an uber-like service where drivers and riders connect directly to one another, without relying on a central third party. After the hackathon, NKN accepted to fund a more advanced prototype, and from there the scope expanded to building a more generic protocol and a suite of open-source software packages that would allow the creation of compatible ride-hailing apps sharing a common pool of users.
Messaging Protocol
The messaging protocol is a key component of the nRide p2p ride-hailing platform, providing a secure and efficient means for riders and drivers to negotiate rides directly without intermediaries. The messaging protocol is built on top of the NKN network, leveraging its unique features to provide a decentralized, scalable, and robust messaging infrastructure. By defining a sequence of messages to be exchanged between riders and drivers, the messaging protocol enables efficient and reliable ride negotiation while ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive information. In this section, we will discuss the technical details of the messaging protocol, including its encryption and security features, reliability and fault tolerance, and integration with the NKN network.
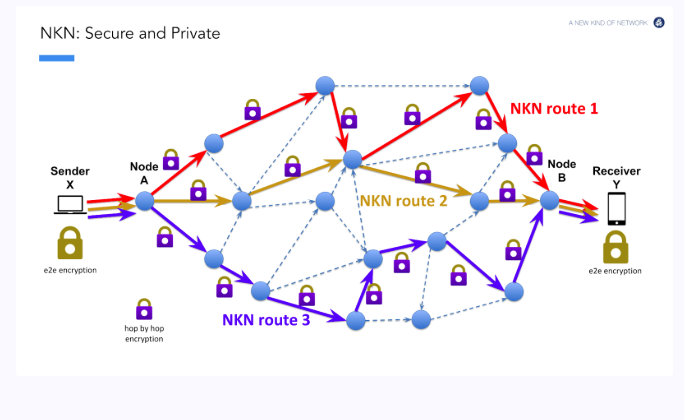
Clients subscribe their NKN ID into their local H3 cell index CosmWasm Contract, to establish encrypted p2p connection between driver and passenger
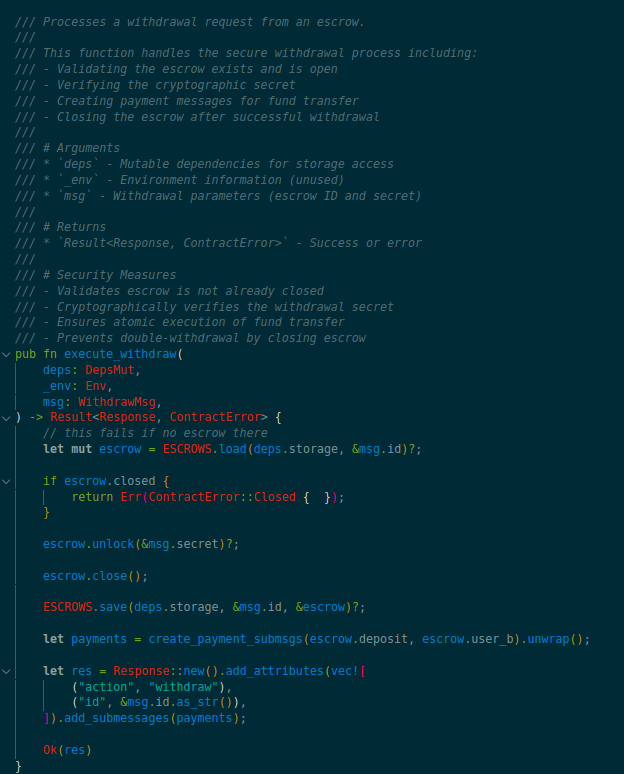
Escrow
Each escrow is composed of two accounts, each guarded by what we call a secret. Once an escrow is funded by both parties, a user must obtain the other user’s secret to unlock all of their deposit, otherwise they will lose a portion of it. In effect, the secret is simply the private component of a cryptographic key pair created for the purpose of the escrow. When a user funds their account in the escrow, they create a new key pair locally, and set the new public key as the ‘lock’ of their account in the escrow. The other user will need to obtain the private key – the secret – to unlock their deposit. Users exchange secrets offline, and the procedure for doing so is not covered by the protocol (could be by tapping phones through NFC, or by sending a message over the NKN network). The escrow smart-contract implements a state machine that guards all possible transitions and outputs given initial configuration and the messages submitted by the users.

Driver Registry
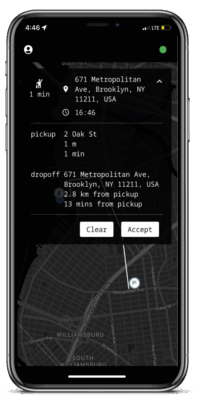
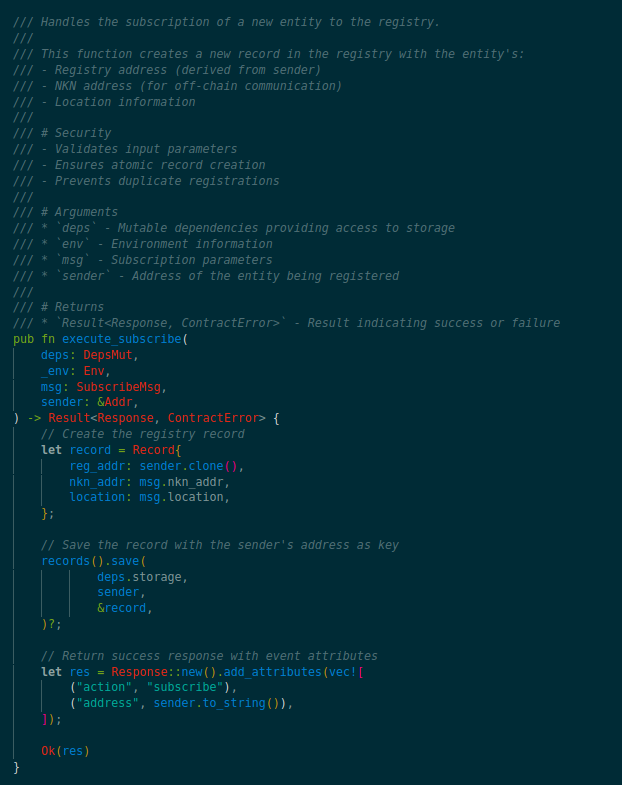
The driver registry is a fundamental component of the nRide protocol that enables riders to discover available drivers in their area. The registry is implemented as a decentralized database using blockchain technology, allowing for secure and transparent storage of driver information. Each driver entry includes their NKN address and an arbitrary location field that can be used to represent their location information in any format, giving maximum flexibility to nRide applications and users. In addition to the location field, driver entries also contain signed certificates indicating their affiliation with specific ride-hailing applications or entities. Drivers can update their location and certificate information on the registry as they move around or change affiliations, allowing riders to easily find nearby drivers and make informed choices about who to ride with.
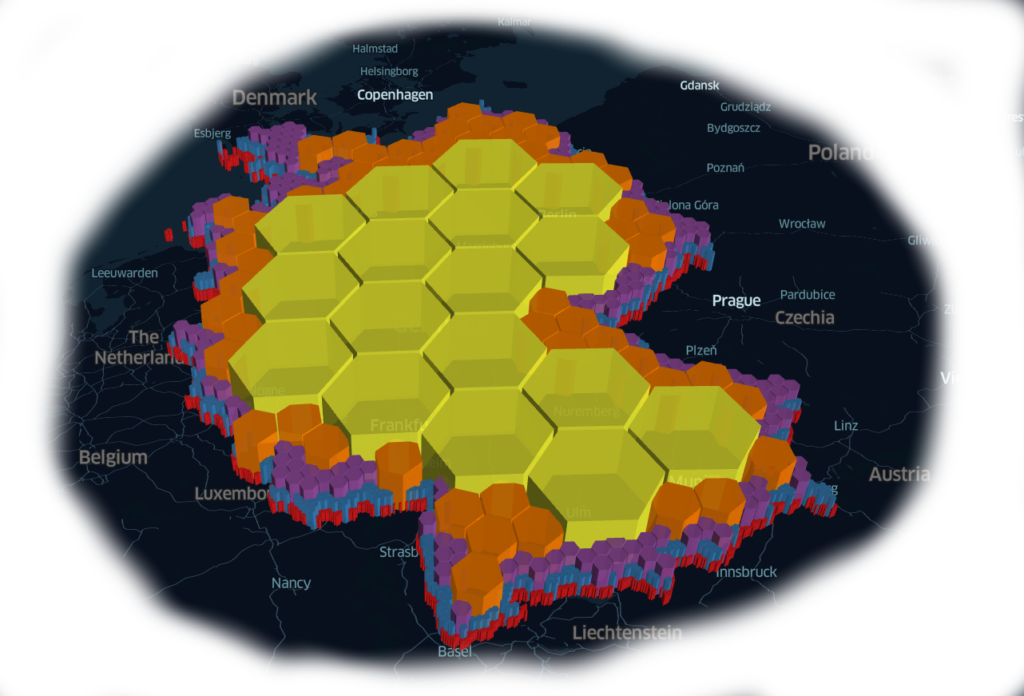
H3 Positioning System
The H3 positioning system is a geospatial indexing system developed by Uber that uses a hexagonal grid to partition the Earth’s surface into well-defined cells. Each cell is identified by a unique H3 index, which enables efficient storage, querying, and processing of geospatial data. The hierarchical structure of H3 allows for varying resolutions, providing a flexible and precise representation of geographic areas.
FAQ
The most frequently asked questions about the world’s first blockchain powered ride-hailing appsuite
Can i already use the app and call for a ride?
Yes and no:
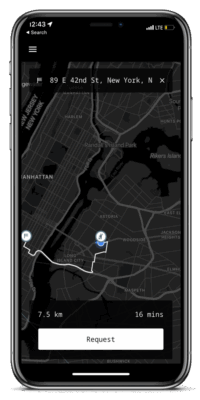
For better understanding you can use the app in free faucet mode: ask a friend to act as driver, and broadcast a ride-request.
I am a Driver or the owner of a taxi company, how can I join the ride-hailing network?
You need to download the Driver’s variant app either from apple appstore or google playstore. You don’t need to register, because the app generates a in-app custodial wallet with a random generated personal seed.
How do I Top-Up my in-app balance?
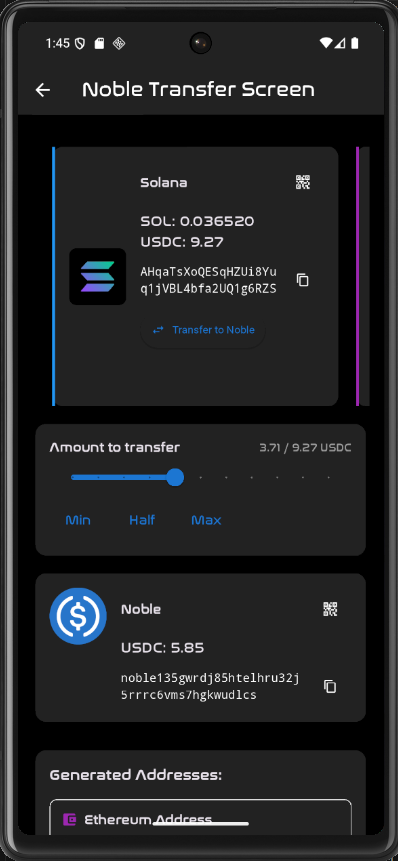
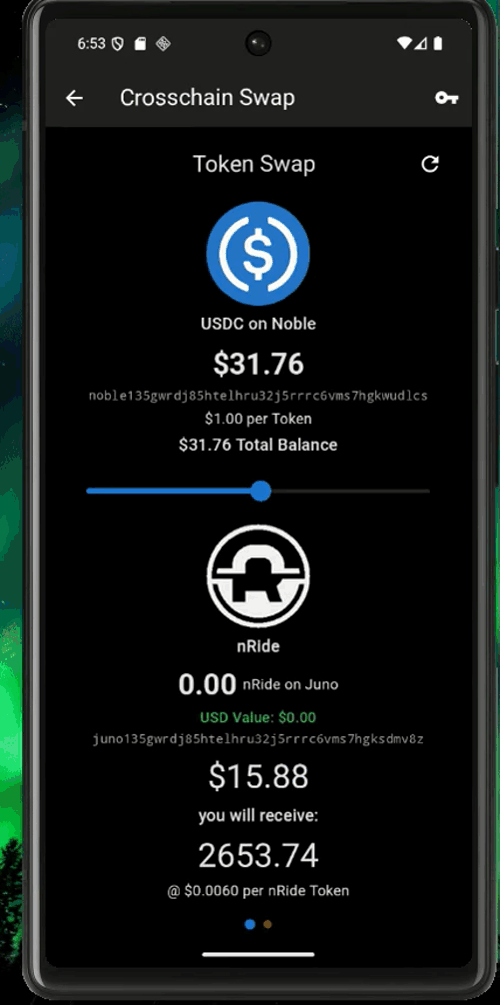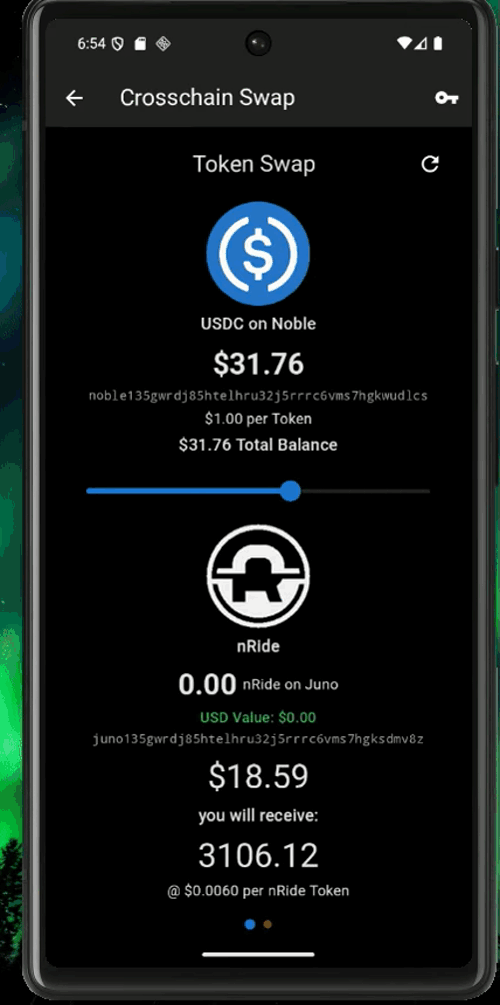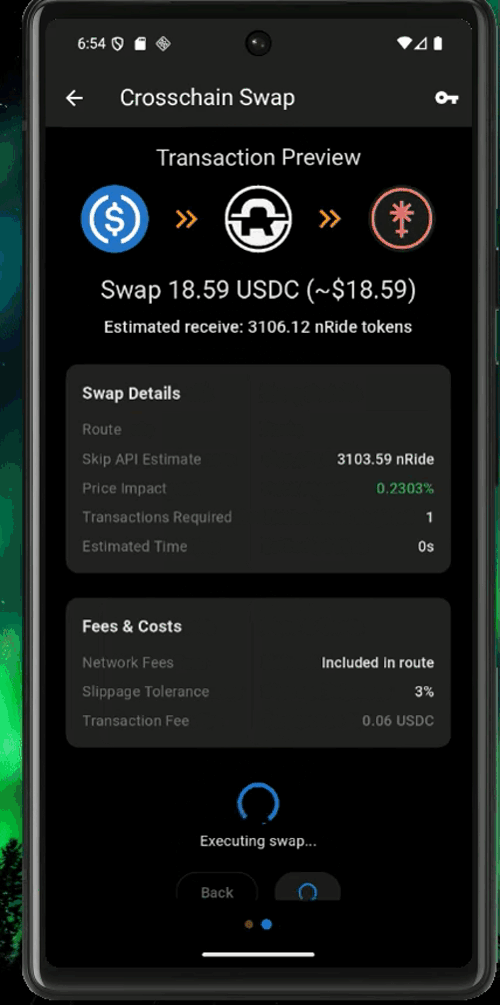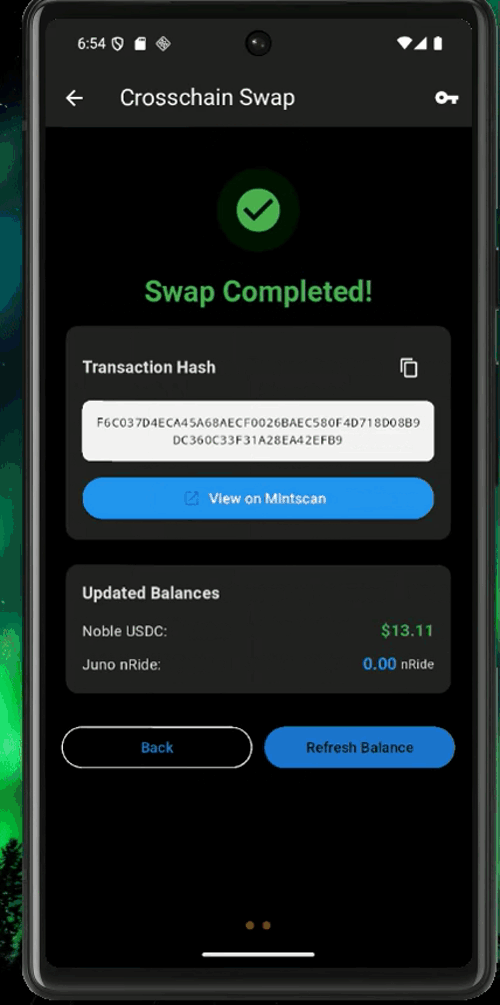
nRide uses interchain USDC, so the easiest way is to use the express.noble.xyz bridge to get USDC from all major blockchains into your app within one click
What blockchain networks are supported?
Currently the supported blockchains are:
Ethereum
Solana
Avalanche
Base
Polygon
ATOM Network
Optimism
Arbitrum
I am a developer, how can i contribute to the project?
nRide is a DAO driven project, so as a contributing developer you will be compensated with project Tokens from the DAO. Please don’t hesitate to get in contact with us, if you think your skills and expertise would be an enrichment for the project’s success

Discover the nRide vision
With its trustless nature and countless possibilities of smart-contract escrows, any taxi company or freelancing driver can participate and benefit from the public DePin Infrastructure provided by the nRide protocol
nRide is the first dedicated multi-chain approach to provide a ride-hailing solution for all personal transporation enterprises, no matter if they are freelancing drivers, gig-economy companies or even global players, looking to extend their coverage. Focusing on compatibility with all major blockchains in the space, nRide will be the tool of choice to take personal mobility into web3